- 图解vllm-原理与架构
- 图解vllm-推理服务与引擎
- 图解vllm-调度器与Block分配
- 图解vllm-执行器与worker
- 图解vllm-model之model和attention_backend
通过上文可以了解到,执行器在调用推理接口后,最终将请求传入worker中的ModelRunner进行推理计算,这时如何使用CUDA加速模型attention和forward的推理。另外,对于我们定制化的model是如何加入到vllm的推理框架来使用的。通过本文你可以了解到这一过程背后的逻辑关系。
1. 模型推理图解
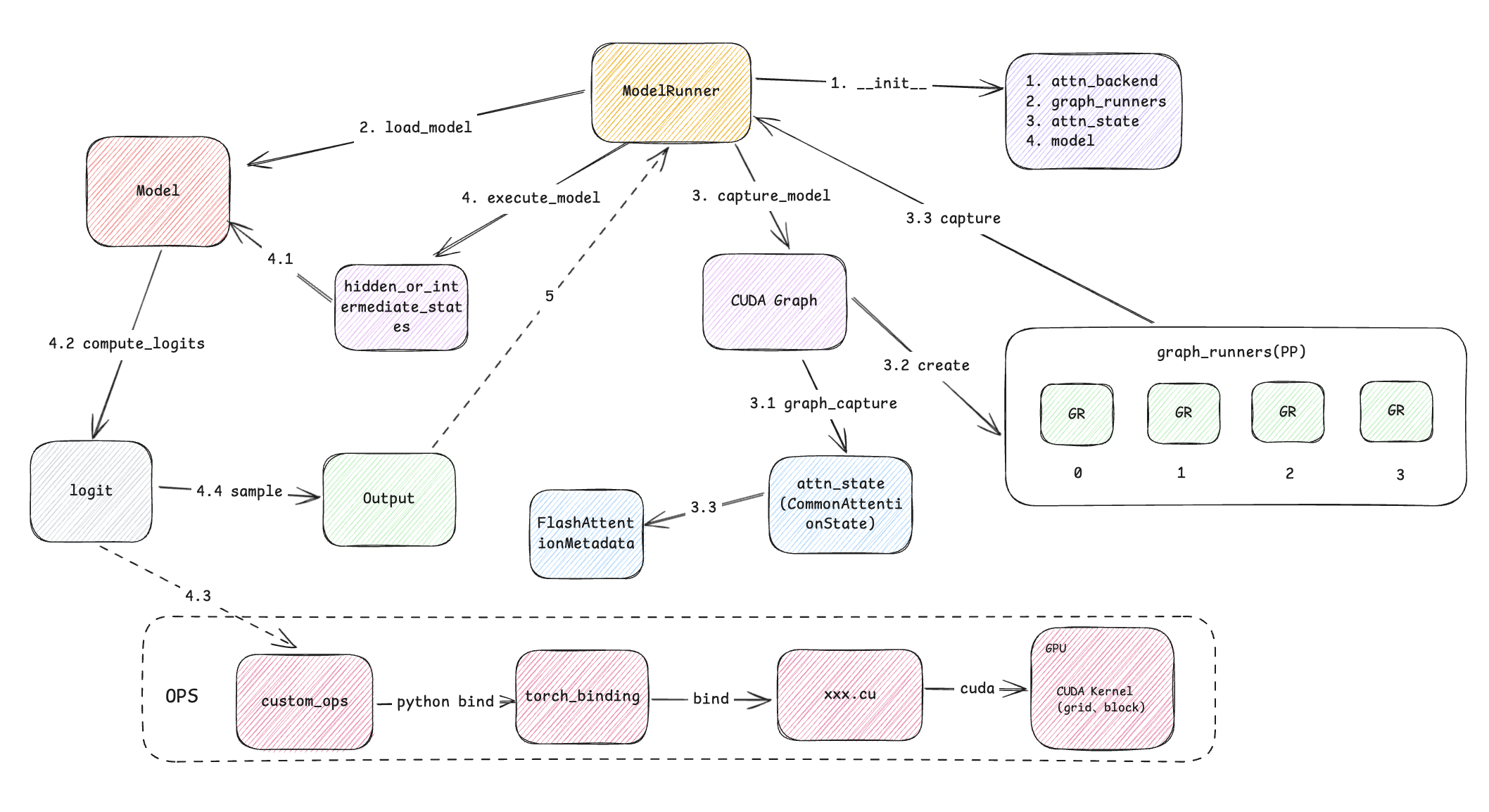
- 从图解中可以看到,ModelRunner拥有attn_backend、graph_runner、att_state、model, 其中attn_backend在不同平台上使用的加速算法;graph_runner主要是在每个Paralletl Pipeline中的推理过程中构建cuda graph优化实例;att_state这个就是attention权重了; model就是我们所说的模型,我们使用其中的forward和sample用于MLP和Token sample策略的输出。
- 调用方法上看,主要分为load_model、capture_model、execute_model三类函数,load_model上篇文章已经讲过,我们针对其他2个方法进行讲解。
2. 模型cuda graph加速
- 上个章节中,capture_model这个方法调用是在initialize_cache(线条3)中进行的,最终在初始化完cache engine后,我们需要使用一个fake的数据对模型进行预热,并构建模型执行推理的时候的CUDA Graph用于加速。
- 我们看一下capture_model的主要流程, 这里主要是通过self.attn_state.graph_capture获取graph_capture_context,包括与GPU通信的steam,在模拟操作过程中,graph会收集所有推理需要的步骤,并进行合理编排,最终返回graph保存在graph_runner中。
@torch.inference_mode()
def capture_model(self, kv_caches: List[List[torch.Tensor]]) -> None:
"""Cuda graph capture a model.
请注意,如果批处理token的数量大于200,则CUDA图的性能增益可以忽略不计。
而且由于CUDA图需要固定大小的张量,因此支持大/可变的批处理大小需要很高的GPU内存开销。
因此,vLLM仅捕获 解码 请求。混合批处理(分块预填充 + 解码)或预填充请求不会被捕获。
由于它仅用于解码,因此它假设批处理中每个序列只有1个token.
"""
start_time = time.perf_counter()
# Prepare dummy inputs. These will be reused for all batch sizes.
max_batch_size = self.max_batchsize_to_capture
# 虚拟推理数据
input_tokens = torch.zeros(max_batch_size, dtype=torch.long).cuda()
input_positions = torch.zeros(max_batch_size, dtype=torch.long).cuda()
if self.model_is_mrope:
input_positions = torch.tile(input_positions, (3, 1))
# Prepare dummy previous_hidden_states only if needed by the model.
# This is used by draft models such as EAGLE.
previous_hidden_states = None
# 模型的实际调用方法中的参数中有previous_hidden_states
if "previous_hidden_states" in inspect.signature(
self.model.forward).parameters:
previous_hidden_states = torch.empty(
[max_batch_size,
self.model_config.get_hidden_size()],
dtype=self.model_config.dtype,
device=self.device)
intermediate_inputs = None
if not get_pp_group().is_first_rank:
intermediate_inputs = self.model.make_empty_intermediate_tensors(
batch_size=max_batch_size,
dtype=self.model_config.dtype,
device=self.device)
# Prepare buffer for outputs. These will be reused for all batch sizes.
# It will be filled after the first graph capture.
# 默认每一个隐藏状态为None
hidden_or_intermediate_states: List[Optional[torch.Tensor]] = [
None
] * self.parallel_config.pipeline_parallel_size
graph_batch_size = self.max_batchsize_to_capture
batch_size_capture_list = [
bs for bs in _BATCH_SIZES_TO_CAPTURE if bs <= graph_batch_size
]
'''
创建graph stream,并返回关联的context
In graph mode, we have to be very careful about the collective
operations. The current status is:
针对custom allreduce和PyNccl开启graph
allreduce \ Mode | Eager | Graph |
--------------------------------------------
custom allreduce | enabled | enabled |
PyNccl | disabled| enabled |
torch.distributed | enabled | disabled|
Note that custom allreduce will have a runtime check, if the
tensor size is too large, it will fallback to the next
available option.
使用 CUDA 图时,我们使用 自定义allreduce内核 或 pynccl。
不使用CUDA 图时,我们使用自定义分布式处理 或 PyTo~rch NCCL
'''
with self.attn_state.graph_capture(
max_batch_size), graph_capture() as graph_capture_context:
# NOTE: Capturing the largest batch size first may help reduce the
# memory usage of CUDA graph.
# 对于每个pp数组执行同样的graph
for virtual_engine in range(
self.parallel_config.pipeline_parallel_size):
# 所有满足graph size的batch size
for batch_size in reversed(batch_size_capture_list):
# FlashAttentionMetadata for CUDA
attn_metadata = (
self.attn_state.graph_capture_get_metadata_for_batch(
batch_size,
is_encoder_decoder_model=self.model_config.
is_encoder_decoder_model))
if self.lora_config:
lora_mapping = LoRAMapping(
**dict(index_mapping=[0] * batch_size,
prompt_mapping=[0] * batch_size,
is_prefill=False))
self.set_active_loras(set(), lora_mapping)
if self.prompt_adapter_config:
prompt_adapter_mapping = PromptAdapterMapping(
[-1] * batch_size,
[-1] * batch_size,
)
self.set_active_prompt_adapters(
set(), prompt_adapter_mapping)
# 先执行forward
# this.graph_runner(...) -> graph_runner.forward(...)
graph_runner = CUDAGraphRunner(
self.model, self.attn_backend.get_name(),
self.attn_state.graph_clone(batch_size),
self.model_config.is_encoder_decoder_model)
capture_inputs = {
"input_ids":
input_tokens[:batch_size],
"positions":
input_positions[..., :batch_size],
"hidden_or_intermediate_states":
hidden_or_intermediate_states[
virtual_engine] # type: ignore
[:batch_size]
if hidden_or_intermediate_states[virtual_engine]
is not None else None,
"intermediate_inputs":
intermediate_inputs[:batch_size]
if intermediate_inputs is not None else None,
"kv_caches":
kv_caches[virtual_engine],
"attn_metadata":
attn_metadata,
"memory_pool":
self.graph_memory_pool,
"stream":
graph_capture_context.stream
}
if previous_hidden_states is not None:
capture_inputs[
"previous_hidden_states"] = previous_hidden_states[:
batch_size]
if self.has_seqlen_agnostic:
# Only used by Mamba-based models CUDA graph atm (Jamba)
capture_inputs.update({
"seqlen_agnostic_capture_inputs":
self.model.get_seqlen_agnostic_capture_inputs(
batch_size)
})
if self.model_config.is_encoder_decoder_model:
# add the additional inputs to capture for
# encoder-decoder models.
self._update_inputs_to_capture_for_enc_dec_model(
capture_inputs)
# capture graph,获取 self._graph, 此时就缓存到runner中了
graph_runner.capture(**capture_inputs)
self.graph_memory_pool = graph_runner.graph.pool()
self.graph_runners[virtual_engine][batch_size] = (
graph_runner)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
elapsed_time = end_time - start_time
# This usually takes < 10 seconds.
logger.info("Graph capturing finished in %.0f secs.", elapsed_time)
- 这里,我们要注意graph_runner.capture(**capture_inputs)这一行,这是生成graph并产生fake hidden states的主要过程
def capture(
self,
input_ids: torch.Tensor,
positions: torch.Tensor,
hidden_or_intermediate_states: Optional[Union[IntermediateTensors, torch.Tensor]],
intermediate_inputs: Optional[IntermediateTensors],
kv_caches: List[torch.Tensor],
attn_metadata: AttentionMetadata,
memory_pool: Optional[Tuple[int, int]],
stream: torch.cuda.Stream,
**kwargs,
) -> Union[torch.Tensor, IntermediateTensors]:
assert self._graph is None
# 运行模型几次而不捕获图表。这是为了确保捕获的图表不包括
# 用于初始基准测试的内核启动,例如,Triton 自动调谐。
# 请注意,一次迭代对于 torch.jit.script 来说是不够的,所以设定_NUM_WARMUP_ITERS为2
for _ in range(_NUM_WARMUP_ITERS):
self.model(
input_ids=input_ids,
positions=positions,
kv_caches=kv_caches,
attn_metadata=attn_metadata,
intermediate_tensors=intermediate_inputs,
**kwargs,
)
# synchronize同步一下上面所有操作,等待完毕.
torch.cuda.synchronize()
# Capture the graph.
# 执行graph, 稍后填充图数据
self._graph = torch.cuda.CUDAGraph()
# 开启graph监控
with torch.cuda.graph(self._graph, pool=memory_pool, stream=stream):
# 执行attention
output_hidden_or_intermediate_states = self.model(
input_ids=input_ids,
positions=positions,
kv_caches=kv_caches,
attn_metadata=attn_metadata,
intermediate_tensors=intermediate_inputs,
**kwargs,
)
if hidden_or_intermediate_states is not None:
if get_pp_group().is_last_rank:
# 在CPU保存hidden_states
hidden_or_intermediate_states.copy_(
output_hidden_or_intermediate_states)
else:
for key in hidden_or_intermediate_states.tensors:
hidden_or_intermediate_states[key].copy_(
output_hidden_or_intermediate_states[key])
else:
hidden_or_intermediate_states = (
output_hidden_or_intermediate_states)
del output_hidden_or_intermediate_states
# make sure `output_hidden_states` is deleted
# in the graph's memory pool
gc.collect()
# 清空操作
torch.cuda.synchronize()
# Save the input and output buffers.
self.input_buffers = {
"input_ids":
input_ids,
"positions":
positions,
"kv_caches":
kv_caches,
**self.attn_state.get_graph_input_buffers(
attn_metadata, self._is_encoder_decoder_model),
**kwargs,
}
if intermediate_inputs is not None:
self.input_buffers.update(intermediate_inputs.tensors)
if get_pp_group().is_last_rank:
self.output_buffers = {
"hidden_states": hidden_or_intermediate_states
}
else:
self.output_buffers = hidden_or_intermediate_states
return hidden_or_intermediate_states
3. 模型执行
- 上文在做测试过程中会执行output_hidden_or_intermediate_states = self.model(…, **kwargs), 这是直接调用模型的forward方法进行推理, 这与模型真正推理是用到的execute_model最终的执行方法一致。我们还是上代码,看注解。
@torch.inference_mode()
#异常装饰函数
@dump_input_when_exception(exclude_args=[0], exclude_kwargs=["self"])
def execute_model(
self,
model_input: ModelInputForGPUWithSamplingMetadata,
kv_caches: List[torch.Tensor],
intermediate_tensors: Optional[IntermediateTensors] = None,
num_steps: int = 1,
) -> Optional[Union[List[SamplerOutput], IntermediateTensors]]:
if num_steps > 1:
raise ValueError("num_steps > 1 is not supported in ModelRunner")
if self.lora_config:
assert model_input.lora_requests is not None
assert model_input.lora_mapping is not None
self.set_active_loras(model_input.lora_requests,
model_input.lora_mapping)
if self.prompt_adapter_config:
assert model_input.prompt_adapter_requests is not None
assert model_input.prompt_adapter_mapping is not None
self.set_active_prompt_adapters(
model_input.prompt_adapter_requests,
model_input.prompt_adapter_mapping)
# cuda graph 空方法,忽略
self.attn_state.begin_forward(model_input)
# Currently cuda graph is only supported by the decode phase.
assert model_input.attn_metadata is not None
prefill_meta = model_input.attn_metadata.prefill_metadata
decode_meta = model_input.attn_metadata.decode_metadata
virtual_engine = model_input.virtual_engine
if prefill_meta is None and decode_meta.use_cuda_graph:
assert model_input.input_tokens is not None
graph_batch_size = model_input.input_tokens.shape[0]
# 这里我们要注意,这个就是上文我们进行预热时获得的graph_runner(CUDAGraphRunner)
# 我们直接拿来加速运行,这时执行runner的forward,最终也是执行self.model中的forward
model_executable = self.graph_runners[virtual_engine][
graph_batch_size]
else:
# 执行model的forward
model_executable = self.model
multi_modal_kwargs = model_input.multi_modal_kwargs or {}
seqlen_agnostic_kwargs = {
"finished_requests_ids": model_input.finished_requests_ids,
"request_ids_to_seq_ids": model_input.request_ids_to_seq_ids,
} if self.has_seqlen_agnostic else {}
if (self.observability_config is not None
and self.observability_config.collect_model_forward_time):
model_forward_start = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
model_forward_end = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
model_forward_start.record()
# 真正执行attention: cuda graph + data
hidden_or_intermediate_states = model_executable(
input_ids=model_input.input_tokens,
positions=model_input.input_positions,
kv_caches=kv_caches,
attn_metadata=model_input.attn_metadata,
intermediate_tensors=intermediate_tensors,
**MultiModalInputs.as_kwargs(multi_modal_kwargs,
device=self.device),
**seqlen_agnostic_kwargs)
if (self.observability_config is not None
and self.observability_config.collect_model_forward_time):
model_forward_end.record()
# Compute the logits in the last pipeline stage.
# 计算attention推理时间
if not get_pp_group().is_last_rank:
if (self.is_driver_worker
and hidden_or_intermediate_states is not None
and isinstance(hidden_or_intermediate_states,
IntermediateTensors)
and self.observability_config is not None
and self.observability_config.collect_model_forward_time):
model_forward_end.synchronize()
model_forward_time = model_forward_start.elapsed_time(
model_forward_end)
orig_model_forward_time = 0.0
if intermediate_tensors is not None:
orig_model_forward_time = intermediate_tensors.tensors.get(
"model_forward_time", torch.tensor(0.0)).item()
hidden_or_intermediate_states.tensors["model_forward_time"] = (
torch.tensor(model_forward_time + orig_model_forward_time))
return hidden_or_intermediate_states
# 获得新鲜的隐藏状态后,我们导入MLP中,得到logits序列
logits = self.model.compute_logits(hidden_or_intermediate_states,
model_input.sampling_metadata)
# Sample the next token.
output: SamplerOutput = self.model.sample(
logits=logits,
sampling_metadata=model_input.sampling_metadata,
)
if (self.observability_config is not None
and self.observability_config.collect_model_forward_time
and output is not None):
model_forward_end.synchronize()
model_forward_time = model_forward_start.elapsed_time(
model_forward_end)
orig_model_forward_time = 0.0
if intermediate_tensors is not None:
orig_model_forward_time = intermediate_tensors.tensors.get(
"model_forward_time", torch.tensor(0.0)).item()
# If there are multiple workers, we are still tracking the latency
# from the start time of the driver worker to the end time of the
# driver worker. The model forward time will then end up covering
# the communication time as well.
output.model_forward_time = (orig_model_forward_time +
model_forward_time)
if self.return_hidden_states:
# we only need to pass hidden states of most recent token
assert model_input.sampling_metadata is not None
indices = model_input.sampling_metadata.selected_token_indices
if model_input.is_prompt:
hidden_states = hidden_or_intermediate_states.index_select(
0, indices)
output.prefill_hidden_states = hidden_or_intermediate_states
elif decode_meta.use_cuda_graph:
hidden_states = hidden_or_intermediate_states[:len(indices)]
else:
hidden_states = hidden_or_intermediate_states
output.hidden_states = hidden_states
return [output]
- 这里model执行的forward不仅使用到了kv_caches, 并且和logits、sample方法一并使用到了cuda原语,这些都是在具体模型中用到的各种Layer、attention层构建是使用的OPS,他们的关系如下:
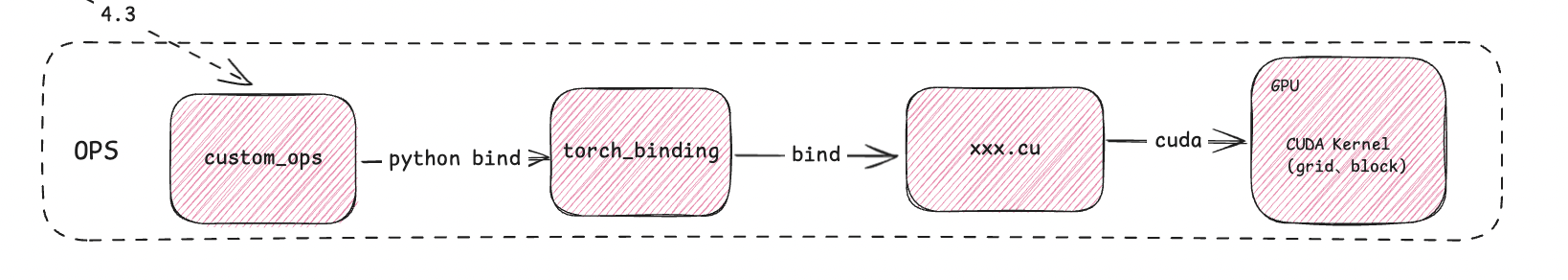
vllm定义实现了custom_ops(vllm/_custom_ops.py)文件,这个文件通过torch_binding引入cpp so库,然后再通过cuda绑定相应的xxx.cu文件,最终执行在GPU上CUDA Kernel方法。这里发方法是具体例如Flash Attention算法的实现地方。后面我会再大模型在并行推理中方法中详细介绍。
4. 总结
本文对模型如何进行cuda graph加速,和模型真正执行时调用链进行了讲解,这里由于我不是研究算法方向,具体模型的架构构成并没有继续研究,不过如果以后有讲过机会会持续的深入学习下去。
随着本章的结束,vllm图解系列文档就到一段路了,我学习transformers到vllm推理和总结大约花了3周时间,平时工作比较忙,也占用了大量的时间,所以一些内容可能只是了解到皮毛,还可能有很多不正确之处,后面会逐步强化这部分的短板,持续精进。
最后,送给自己一句教员说过的一句话: 不为敌之其势汹汹所吓倒,不为尚能忍耐的困难所沮丧,不为某些挫折而灰心,给予必要的耐心和持久,是完全必要的。
共勉